
glm lenses ib1.carrot, fam(bin) nolog eform Here is the logistic regression with just carrot as the predictor: glm lenses ib1.carrot, fam(bin) nolog Since command glm will be used to calculate the RR, it will also be used to calculate the OR for comparison purposes (and it gives the same results asĬommand logit). We could use either command logit or command glm to calculate It is interesting that fewer people with the carrot-loving gene needed corrective lenses (especially since Of carrot and lenses, which will allow us to calculate the unadjusted OR and RR So if we want to talk about whether the carrot-loving gene, gender, or latitude is associated with the risk of requiring corrective lenses by the age of 30, then relative risk is a more appropriate measure than the odds ratio. Variable name type format label variable label Here’s a quick description of the variables. The data set isĮyestudy.dta in Stata 8 format. Values (N=100) were assigned using a random number generator. Of the continental US they lived on the longest (24 to 48 degrees north). We also noted their gender (= 1 if female, = 2 if male), and what latitude (assume not having this gene results in the opposite), and that we screenedĮveryone for this carrot gene at baseline (carrot = 1 if they have it, = 0 if Having a gene which causes one to have a lifelong love and craving for carrots Suppose we wanted to know if requiring corrective lenses is associated with Tumors or other major health problems during the 20 years between assessments. Assume none of them have had serious head injuries or had brain Study participants require corrective lenses by the time they are 30 years old.Īssume all participants do not need them at a baseline assessment when they areġ0 years old. The outcome generated is called lenses, to indicate if the hypothetical Example Data: OddsĪ hypothetical data set was created to illustrate two methods of estimating relative risks using Poisson regression model with a robust error variance.
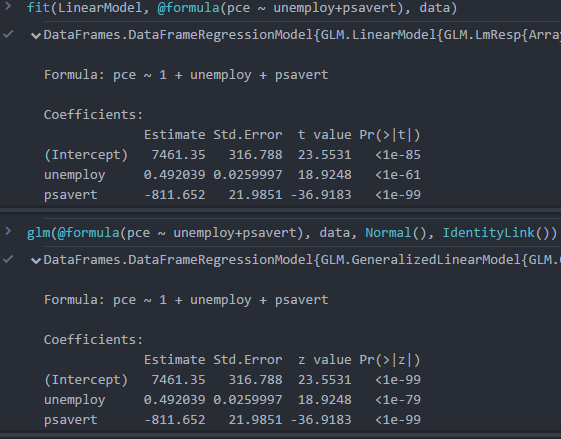
One estimates the RR with a log-binomial regression model, and the other uses a These methods will be demonstrated here using hypothetical data created for this
#STATA GLM HOW TO#
There are several options for how to estimate RRs directly in Stata. Here the purpose is to demonstrate methods for calculating the RR, assuming that it is the appropriate thing to do. There are some who hold the opinion that the OR should be used even when the outcome is common, however (). Several articles in recent medical and public health literature point out that when the outcome event is common (incidence of 10% or more), it is often more desirable to estimate an RR since there is an increasing differential between the RR and OR with increasing incidence rates, and there is a tendency for some to interpret ORs as if they are RRs (-). Although this is often appropriate, there may be situations in which it is more desirable to estimate a relative risk or risk ratio (RR) instead of an odds ratio (OR). Introductionīinary outcomes in cohort studies are commonly analyzed by applying a logistic regression model to the data to obtain odds ratios for comparing groups with different sets ofĬharacteristics. To Karla for taking the time to develop this page and giving us Statistician in the Division of Geriatrics at UCSF. This page was developed and written by Karla Lindquist, Senior


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
